Looking for a way to add some extra flavor to your cooking? Why not try growing your own mushrooms! Mushrooms are a delicious and versatile ingredient that can be used in all sorts of dishes. Plus, they’re really easy to grow, even if you don’t have a lot of space.
How are mushrooms grown commercially
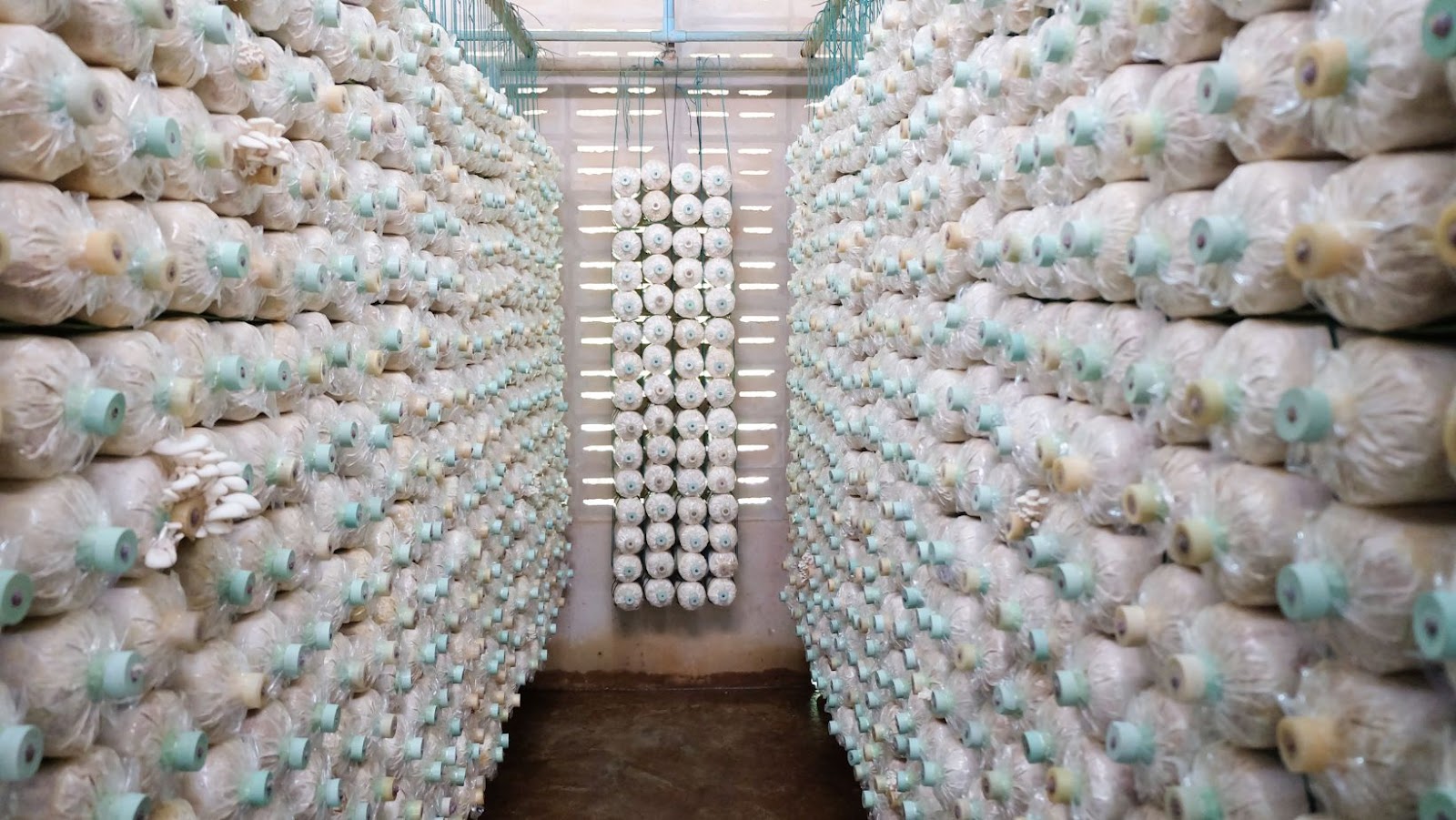
Mushrooms are a type of fungi, and like all fungi, they grow by consuming organic matter. In the wild, they break down fallen leaves and dead trees. In commercial mushroom farms, the substrate (what the mushrooms grow in) is usually a mix of straw and manure.
The substrate is first pasteurized to kill off any harmful bacteria or fungi. Once it has cooled, spawn (mushroom seeds) are mixed in. The spawn will colonize the substrate and eventually produce mushrooms.
Mushrooms are grown in chambers called fruiting rooms, where the temperature and humidity can be controlled. These conditions encourage the development of fruit bodies (the mushrooms themselves). After a few weeks, the mushrooms are ready to harvest.
The benefits of growing your own mushrooms
There are many benefits to growing your own mushrooms, including the improved flavor of homegrown mushrooms and the satisfaction of being able to harvest them yourself. In addition, growing your own mushrooms can save you money. Commercial mushrooms are often grown in huge quantities and shipped long distances, so they can be expensive. By growing your own, you can get delicious mushrooms at a fraction of the cost.
If you’re interested in trying your hand at growing mushrooms, there are a few things you should know. First, you’ll need to choose the right type of mushroom for your climate and conditions. Not all mushrooms will grow well in all environments, so it’s important to do some research ahead of time. You’ll also need to be diligent about sanitation and make sure that your grow area is free of contaminants. With a little knowledge and effort, you can enjoy delicious home grown mushrooms in no time!
The best mushroom species for home cultivation
Mushrooms are a type of fungus that grows in the soil, on trees or on decaying organic matter. There are many different species of edible mushrooms, and the best mushrooms for home cultivation depend on your personal preferences.
Some easy-to-grow mushrooms include oyster mushrooms, white button mushrooms and shiitake mushrooms. Oyster mushrooms can be grown on a variety of substrates, such as straw or coffee grounds, and they have a mild flavor that pairs well with other ingredients. White button mushrooms are the most common type of mushroom in grocery stores, and they can be easily cultivated in a sterile environment. Shiitake mushrooms have a more robust flavor than other types of cultivated mushrooms, and they can be grown on logs or wooden boards.
If you are interested in growing your own mushrooms at home, it is important to start with sterile spores or spawn. Once you have obtained spores or spawn, you will need to prepare a suitable substrate for mushroom growth.Spawn can be mixed into the substrate material or placed on top of it; when using the latter method, the spawn should be covered with a layer of plastic to prevent it from drying out. Once the substrate is prepared, it should be kept at a temperature between 60-70 degrees Fahrenheit and placed in an area with high humidity until the mushrooms begin to fruit.
The simplest way to grow mushrooms at home
Mushrooms are a type of fungi that lack chlorophyll and thus cannot produce their own food through photosynthesis like plants do. Because of this, mushrooms must decompose organic matter to acquire the nutrients they need to grow. This makes them perfect candidates for recycling programs as they can help turn household and agricultural waste into a valuable product.
Mushrooms are grown in controlled environments on substrates that provide the necessary nutrients for fungi to grow. The type of substrate used will depend on the mushroom species being cultivated. For example, oyster mushrooms can be grown on straw while shiitake mushrooms prefer hardwood logs.
Mushroom farmers will often start with what is known as spawn, which is simply mushroom mycelium (the vegetative growth stage of a fungus) grown on an inert substrate like rye grain. Spawn is used to inoculate the desired substrate, which is thenIncubated under conditions that favor mushroom growth. Once the substrate has been fully colonized by the mycelium, it is time to fruit the mushrooms.
Fruiting can be induced by a number of environmental factors, including changes in temperature, humidity, and air exchange. After fruiting has begun, it is important to maintain these ideal conditions or else the mushrooms will not continue to grow properly. Once they have reached maturity, the mushrooms are harvested and sold fresh or dried.
Tips for successful mushroom cultivation
Mushroom cultivation is a process where mushrooms are grown commercially for food production. It requires specialized equipment and knowledge to ensure a consistent product. There are four main steps in mushroom cultivation: spawning, casing, fruiting and harvesting.
1. Spawning: This is the process of introducing the mushroom spores into the substrate. The substrate is usually a mixture of peat, compost and other organic materials. The spawn is mixed with the substrate and then placed in incubation rooms. These rooms are kept at a warm temperature and high humidity to encourage the spores to germinate.
2. Casing: Once the spawn has colonized the substrate, it is time to case it. Casing is a layer of material placed on top of the substrate to provide an environment that encourages fruiting. The most common type of casing is peat-based.
3. Fruiting: Once the casing has been applied, the substrate will be allowed to fruit. Fruiting is when the mushrooms actually form. The conditions in the fruiting room are different to those in the incubation room; they are warmer and more humid. This encourages the formation of mushrooms.
4 Harvesting: After around two weeks, the mushrooms will be ready to harvest. They should be picked when they are still young and before they open up fully. Mushrooms can be harvested by hand or using specialized equipment
The most common problems with mushroom cultivation
Mushrooms are a healthy and delicious addition to any meal, but they can be tricky to grow at home. Here are some of the most common problems with mushroom cultivation, and how to avoid them.
1. Lack of light: Mushrooms need plenty of light to grow, so make sure they are getting at least 12 hours of direct sunlight per day. If they are not getting enough light, they will become leggy and produce fewer mushrooms.
2. Lack of humidity: Mushrooms need high humidity to grow properly, so make sure the growing area is always moist. A humidifier can help maintain the proper level of humidity.
3. Too much water: Mushrooms do not like to be waterlogged, so make sure the growing medium is well-drained. If the mushrooms are sitting in water, they will rot and die.
4. Temperature fluctuations: Mushrooms prefer a steady temperature between 60-70 degrees Fahrenheit. Sudden changes in temperature can shock the mushrooms and stunt their growth.
5. Pests: Mice, rats, and other pests are attracted to mushroom crops, so it is important to keep the growing area clean and free of debris. Pest control measures such as traps or bait stations may also be necessary.
How to harvest and store your mushrooms
Harvesting and storing your mushrooms properly is important to ensure that they stay fresh and edible for as long as possible. Here are some tips on how to harvest and store your mushrooms:
-Harvest mushrooms when they are young and have not yet started to produce spores. This will typically be when the cap is still closed.
-Cut the mushroom at the base of the stem using a sharp knife or scissors. Avoid pulling the mushroom out by the stem, as this can damage the mushroom and make it more susceptible to rot.
-Place harvested mushrooms in a paper bag or container with holes in it so that they can breathe. Do not store them in a sealed container or plastic bag, as this will cause them to spoil more quickly.
-Store mushrooms in a cool, dark place, such as a refrigerator, until you are ready to use them. Most mushrooms will stay fresh for 2-3 days when stored correctly.
Recipes for delicious mushroom dishes
The Recipes for delicious mushroom dishes guide provides instructions on how to cook various types of mushrooms. This guide also includes tips on how to select the right mushroom for the dish, as well as how to store mushrooms.
The health benefits of mushrooms
Mushrooms are low in calories and fat, but they are a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including selenium, potassium, phosphorus, and vitamin B5. They also contain antioxidants that may protect against cell damage.
Mushrooms are a good source of protein, especially for vegetarians and vegans. They contain all the essential amino acids our bodies need to build and maintain muscle tissue.
Eating mushrooms may boost your immune system. Mushrooms are a rich source of polysaccharides – a type of carbohydrate that the body uses to produce antibodies. Antibodies are part of the immune response that helps fight off infection.
Interesting facts about mushrooms
Mushrooms are a type of fungi. There are more than 14,000 species of mushrooms, but only about 10% of those are edible. The rest can cause everything from digestive upset to death.
Some interesting facts about mushrooms:
-Mushrooms are low in calories and fat. They’re also a good source of fiber, potassium, and B vitamins.
-The average American only eats about 4 pounds of mushrooms per year. Compare that to the 20 pounds per year that the average Italian eats!
-White button mushrooms make up 90% of the mushrooms consumed in the US. However, there are many other varieties available including shiitake, oyster, crimini, portobello, and more.
-A mushroom is not a plant because it doesn’t have chlorophyll to make its own food from sunlight like plants do. Mushrooms grow best in damp, dark places.
-Mushrooms can be canned, frozen, or dried for future use.